GeomBD3
Introduction
Requirements
Downloads
Installation
User Guide
References
Introduction
GeomBD3 is a rigid body Brownian dynamics software package for simulating association rates and molecular recognition in biological or engineered systems. GeomBD3 provides users with a robust tool for rapidly simulating practically any system under a range of conditions. The program supports many combinations of ligand starting conditions, boundary conditions, and cell shapes to make modeling of diverse environments possible. This also allows for better comparison with experiment or theory.
A GeomBD3 simulation consists of two main parts: (1) a ligand and (2) one or more receptor molecules. During simulation, many ligand replicates diffuse in parallel among the stationary, grid-based descriptions of the receptor system. Generally, the smaller of the two binding molecules should be chosen as the ligand since simulation time scales linearly with ligand size. However, the ligand need not be a small molecule. The receptor comprises all parts of the system that are not the ligand.
Simulations can be run in multiple configurations. The default configuration takes place under completely user-defined conditions. The program also supports the NAM configuration for determining second-order association rate constants. Finally, GeomBD3 can extend the NAM scheme to quantify direct and indirect substrate transfer rates in multi-enzyme complexes. Association rates, binding pathways, diffusion coefficients, non-specific association sites, and more can be calculated from any simulation type.
The following features are included in GeomBD3:
- Simple rigid body ligand PQR-formatted definitions composed of charged spherical particles.
- Plain-text atom and molecule parameter files for easy modification to allow simulation of novel systems.
- Script to automatically parameterize ligand and receptor molecules
- Volume exclusion grids for receptor representation.
- Precalculated electrostatic grid support for inclusion of electrostatic forces via the screened Coulomb potential.
- Precalculated Lennard-Jones potential grid support for inclusion of attractive dispersion forces and repulsive atomic overlap.
- Precalculated ligand desolvation potential grid for the energy associated with stripping water from a ligand upon binding.
- Linearly variable timestep for efficiency.
- Reaction criteria defined by distance threshold between ligand atom(s) and binding site coordinate(s).
- Multiple combinations of ligand starting conditions, boundary conditions, and cell shapes.
- Traditional NAM method for association rate constant determination.
- Inter-receptor transfer simulations using a split scheme determining "direct" and "indirect" contributions to intermediate transfer rate
- Automated termination of simulation sets via convergence criteria.
- Intel Cilk+ threaded parallel simulation.
Requirements
To Run the package
- Linux or Unix-like operating system
- Python2.6+ for supporting analysis scripts
To modify and compile the source code
- Intel oneAPI Base Toolkit with Add-on oneAPI HPC Toolkit
Downloads
- GeomBD3 - Stabilized GeomBD version 3
- GitHub - GeomBD3 package and other analysis codes for specific projects/systems
Installation
- $unzip GBD3_master.zip
- export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=path to GBD3_master/GBD3_master/Example/intel_cilk
User Guide
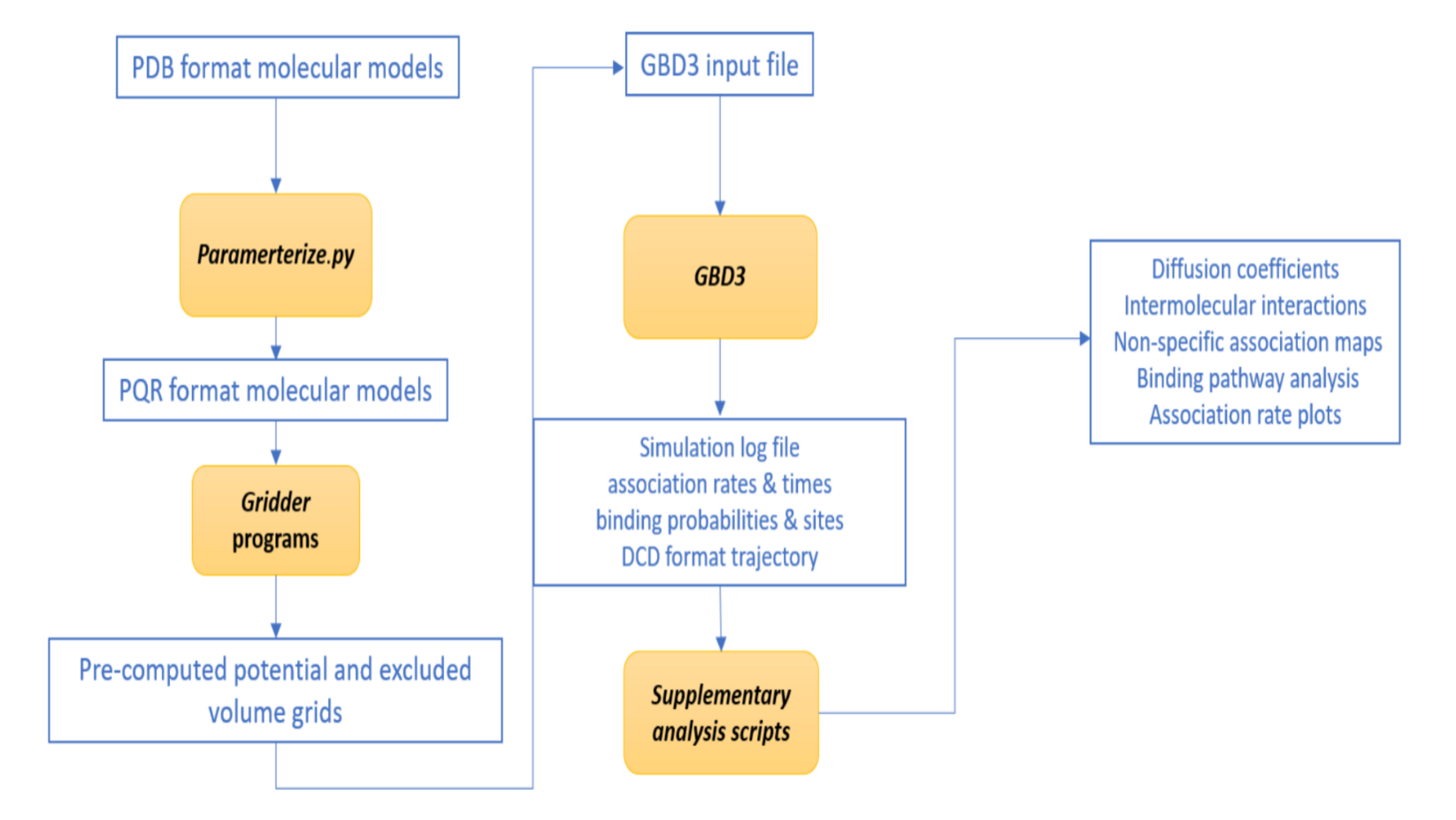
Input File Keywords and Examples
GeomBD can be run using the following example command:
GBD -i INPUT_FILE -l LOG_FILE_BASE -o TRAJ_FILE_BASE
A GeomBD3 simulation can be restarted using the following example command:
GBD -i INPUT_FILE -l LOG_FILE_BASE -o TRAJ_FILE_BASE -c TRAJ_FILE_BASE.crd -t TRAJ_FILE_BASE.t
References
[1] Timothy Cholko, Shivansh Kaushik, Kingsley Wu, and Chia-en A. Chang, GeomBD3: Brownian Dynamics Simulation Software for Biological and Engineered Systems, 2022[link][2] Roberts, C. C. and Chang, C-E. A.*, Modeling of Enhanced Catalysis in Multi-enzyme Nanostructures: Effect of Molecular Scaffolds, Spatial Organization, and Concentration. J. of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2015 [link]
[3] Roberts, C. C. and Chang, C-E. A.*, Analysis of Ligand-Receptor Association and Intermediate Transfer Rates in Multi-enzyme Nanostructures with All-Atom Brownian Dynamics Simulations. J. of Physical Chemistry B. 2016 [link]